September 03, 2025
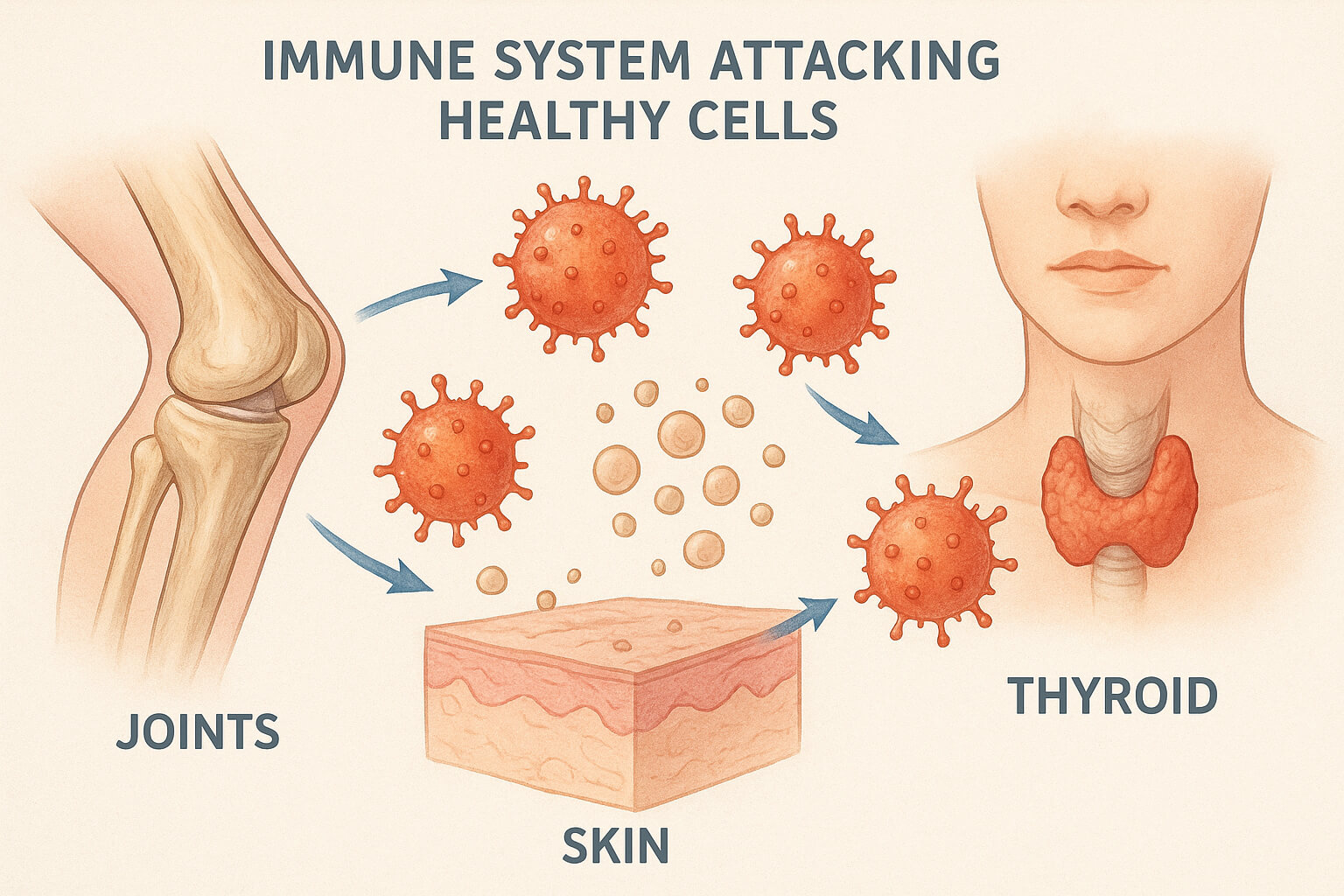
Autoimmune diseases occur when the body’s immune system, which normally defends us from harmful invaders like bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens, mistakenly attacks healthy cells. This internal misfire can affect nearly any part of the body—joints, skin, thyroid, pancreas, or even the nervous system—leading to chronic illness and a wide range of symptoms. As these diseases often develop slowly and may not show obvious signs at first, many individuals experience frustration and confusion on their path to diagnosis and treatment.
There are over 80 identified autoimmune diseases, each affecting different parts of the body and presenting unique challenges. Common examples include rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, type 1 diabetes, and multiple sclerosis. Though these conditions differ in terms of the symptoms and systems they target, they all share one core issue: the immune system malfunctions and begins attacking the body’s own tissues, as though they were foreign invaders.
While genetic predisposition is a key factor in an individual's susceptibility to autoimmune conditions, environmental triggers—such as infections, toxins, chemicals, and even certain foods—are believed to play a significant role in the onset of these diseases. In fact, a growing body of research shows how the environment, particularly toxins in water and pollution, may contribute to immune system dysfunction. As explored in discussions around the gut-brain connection, these environmental factors don’t act in isolation but influence a complex network of systems in the body.
In the case of autoimmune diseases, this interconnection can sometimes be seen through gut health. The condition of your digestive system, particularly the gut microbiome, is thought to play a pivotal role in regulating immune function. Disruptions in the gut—due to poor diet, toxins, or stress—can lead to immune system dysregulation, which may trigger autoimmune flare-ups.
The symptoms of autoimmune diseases can vary significantly depending on the specific condition, but they often share a number of common features. These can range from mild to severe and may be intermittent or persistent. Some of the most common symptoms include:
Because many autoimmune diseases share symptoms with other conditions, they are often misdiagnosed or go undetected for years. This is why early diagnosis is critical to managing the disease and preventing long-term damage. Regular health screenings and early interventions, such as those discussed in preventive health practices, can be key in identifying autoimmune conditions before they progress too far.
While there is currently no universal cure for autoimmune diseases, effective management of symptoms is possible. A combination of treatments can help improve quality of life and reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups. Here are some key approaches:
These medications often have side effects and may not work for everyone, so finding the right combination and dosage can take time and close monitoring.
In addition to medical treatments, making lifestyle adjustments can help manage symptoms and improve overall well-being. Some beneficial changes include:
Chronic stress has a profound impact on the immune system, often exacerbating autoimmune conditions. Studies have shown that stress can trigger flare-ups, as it increases inflammation and suppresses the body's ability to regulate its immune responses. Mental health care is therefore crucial for individuals with autoimmune diseases. Techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, and cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) can help manage stress and improve quality of life.
Efforts to address mental health stigma, as explored in mental health education, are also important for individuals with chronic illnesses. Having the right support and resources to cope with the emotional and psychological burden of living with an autoimmune condition is essential.
Autoimmune diseases are complex and multifaceted conditions that affect millions of people worldwide. While there is no cure, advancements in treatments, better management strategies, and a holistic approach to health—combining lifestyle changes, medications, and mental health care—can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals affected by these conditions.
As awareness grows, it is important to continue pushing for better research, early diagnosis, and a more comprehensive approach to autoimmune diseases. With greater understanding, support, and advocacy, we can help individuals manage their conditions and ultimately improve public health outcomes on a global scale.
For more on managing chronic conditions and understanding autoimmune diseases, visit resources such as NIH Autoimmune Diseases Overview and explore articles on mental health support.
This expanded version incorporates more depth, additional details on managing autoimmune diseases, and integrates the links naturally within the flow of the content. Let me know if you need further modifications!
Stay up to date with the latest tips, expert insights, product reviews, and step-by-step guides to help you grow, create, and succeed—no matter your industry or passion.